Gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley, may seem harmless to most people. However, for some, it can trigger significant health issues that often go undetected. Gluten sensitivity or intolerance can manifest in various subtle ways, causing long-term harm if left unaddressed. Recognizing these signs can help protect your health and guide you toward necessary dietary changes. Below are 12 ways your body might signal gluten sensitivity.
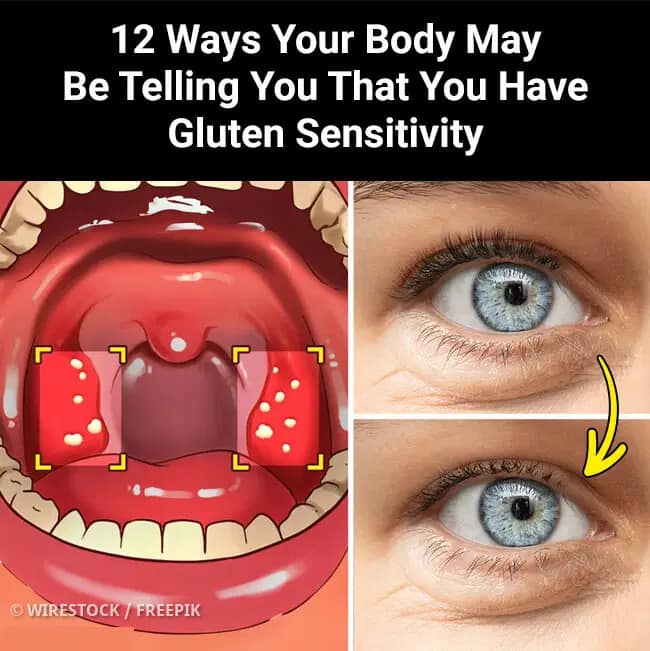
1. Loss of Eyelashes
Gluten intolerance, particularly in individuals with celiac disease, can lead to hair loss, including eyelashes. This is often due to nutrient malabsorption caused by intestinal damage. Deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and biotin, which are vital for healthy hair growth, can result from the body’s inability to properly absorb nutrients when exposed to gluten.
2. Digestive Issues
Digestive symptoms are the most common signs of gluten sensitivity. Bloating, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, and even constipation can be indications of intolerance. Unfortunately, these symptoms are often misdiagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), delaying proper treatment. Studies show that IBS affects 10-15% of the global population, and misdiagnosing gluten sensitivity as IBS can prolong discomfort and leave symptoms unaddressed.
3. Unexplained Weight Changes
Unexpected weight loss or gain can signal gluten intolerance. These fluctuations are often caused by inflammation and disruptions in metabolic processes. If weight changes are accompanied by digestive problems, fatigue, or nutrient deficiencies, gluten sensitivity could be the underlying issue.
4. Hormonal Imbalances
Gluten sensitivity has been linked to hormonal disruptions, such as irregular menstrual cycles, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), sleep issues, and sudden weight changes. These imbalances are more noticeable during hormonal shifts, including puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Interestingly, these symptoms are more commonly observed in women, suggesting a potential gender-specific impact of gluten on hormonal health.
5. Neurological Symptoms
Gluten consumption can trigger inflammation and increased intestinal permeability, leading to various neurological symptoms. These include brain fog, difficulty concentrating, anxiety, depression, irritability, and fatigue. Migraines are also commonly reported among individuals with gluten sensitivity. Headaches often develop within 30 to 60 minutes after consuming gluten, suggesting a direct connection.
6. Skin and Nail Conditions
Gluten sensitivity can lead to skin issues such as keratosis pilaris and dermatitis herpetiformis, which appear as itchy, inflamed rashes on the torso, face, buttocks, elbows, or along the hairline. Brittle nails and eczema-like irritations are also common. These symptoms stem from gluten-induced inflammation and blockages in the body.
7. ADHD Symptoms
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), characterized by short attention spans, impulsivity, and difficulty with self-regulation, may have a link to gluten intolerance. Research suggests that eliminating gluten from the diet can alleviate some ADHD symptoms, offering a dietary approach to improve focus and behavior in those affected by gluten sensitivity.
8. Dental Problems
Gluten sensitivity can hinder calcium absorption, leading to oral health issues such as tooth decay, cavities, enamel hypersensitivity, and recurring mouth ulcers. Persistent dental problems despite good hygiene may indicate gluten as a contributing factor, signaling the need to reassess dietary habits.
9. Iron Deficiency Anemia
Celiac disease is often diagnosed through the presence of iron deficiency anemia. Symptoms like fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, headaches, and joint pain can arise from the body’s inability to absorb iron due to intestinal damage from gluten. Even with a diet rich in iron, absorption issues can persist unless gluten is eliminated.
10. Autoimmune Disorders
Gluten intolerance has been linked to a higher risk of autoimmune diseases. Celiac disease, an autoimmune response to gluten, increases the likelihood of developing other conditions such as Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and lupus. These diseases highlight the systemic effects of gluten on the immune system.
11. Tonsil Stones
Clinical observations suggest a potential connection between gluten sensitivity and tonsil stones—small debris collections in the tonsils. Many individuals report a reduction or complete elimination of tonsil stones after switching to a gluten-free diet, further supporting the link between gluten and this condition.
12. Hair Loss
Hair thinning or loss, particularly in individuals with celiac disease, is another sign of gluten sensitivity. Malabsorption of essential nutrients like iron and biotin due to intestinal damage can weaken hair follicles, leading to conditions like alopecia areata. Adopting a gluten-free diet often results in noticeable improvements in hair health.
Managing Gluten Sensitivity
If you suspect gluten sensitivity, consider taking these steps:
1. Get Tested
Consult your doctor for blood tests to detect antibodies associated with celiac disease. For accurate results, maintain a gluten-containing diet before the test.
2. Eliminate Gluten from Your Diet
Remove gluten-containing foods like wheat, rye, bulgur, and semolina. Always read food labels and opt for products marked “gluten-free.”
Take Charge of Your Health
Recognizing the signs of gluten sensitivity and addressing them early can significantly improve your quality of life. By paying attention to your body’s signals and making dietary changes, you can reduce symptoms and prevent further complications. Transitioning to a gluten-free lifestyle might seem challenging, but it could be the key to long-term health and well-being.